함수형 컴포넌트 State
Class Component
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| import React, { Component } from 'react'
export default class ClassComponent extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = { date: new Date() }
}
componentDidMount() {
this.timerID = setInterval(() => this.tick(), 1000)
}
componentWillUnmount() {
clearInterval(this.timerID)
}
tick() {
this.setState({
date: new Date(),
})
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1>Hello, world! Class Component</h1>
<h2>It is {this.state.date.toLocaleTimeString()}.</h2>
</div>
)
}
}
|
Functional Component
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| import React, { useEffect, useState } from 'react'
export default function FunctionalComponent() {
const [date, setDate] = useState(new Date())
const tick = () => {
setDate(new Date())
}
useEffect(() => {
const interval = setInterval(() => tick(), 1000)
return () => {
clearInterval(interval)
}
}, [])
return (
<div>
<h1>Hello, world! It's Functional</h1>
<h2>It is {date.toLocaleTimeString()}.</h2>
</div>
)
}
|
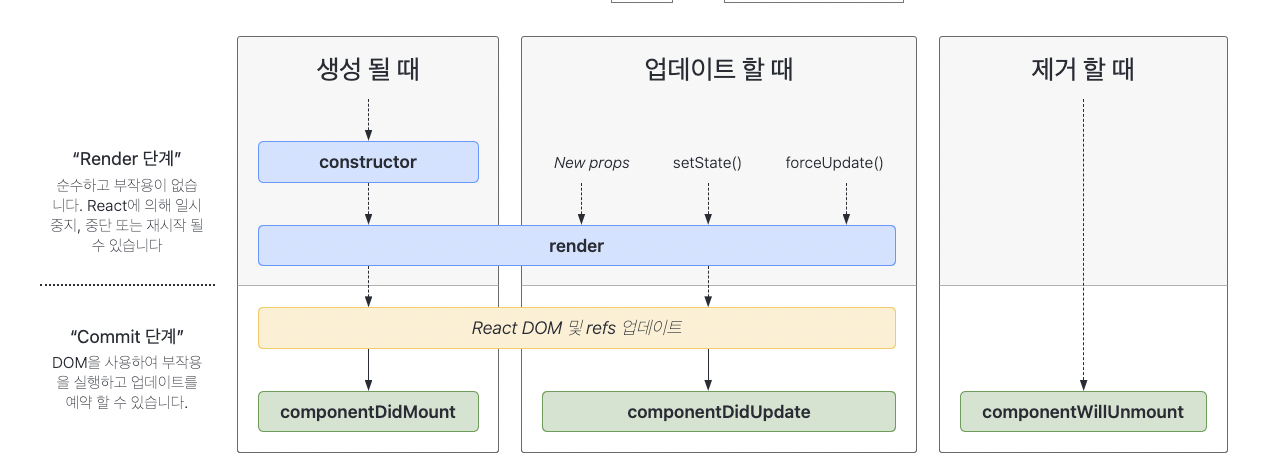
컴포넌트 생명주기
https://ko.reactjs.org/docs/react-component.html
- 마운트 - 메서드들은 컴포넌트의 인스턴스가 생성되어 DOM 상에 삽입될 때에 순서대로 호출
- constructor()
- render()
- componentDidMount()
- 업데이트 - Props 또는 state가 변경되면 갱신이 발생. 컴포넌트가 다시 렌더링될때 순서대로 호출
- render()
- componentDidUpdate()
- 마운트 해제 - 컴포넌트가 DOM 상에서 제거될 때에 호출
https://projects.wojtekmaj.pl/react-lifecycle-methods-diagram/
생명주기 도표
합성 이벤트
https://ko.reactjs.org/docs/handling-events.html
- React 엘리먼트에서 이벤트를 처리하는 방식은 DOM엘리먼트에서 이벤트를 처리하는 방식과 매우 유사하지만 , 몇 가지 문법 차이가 있다
- React의 이벤트는 소문자 대신 캐멀 케이스(camelCase)를 사용한다.
- JSX를 사용하여 문자열이 아닌 함수로 이벤트 핸들러를 전달한다.
- React에서는 false를 반환해도 기본 동작을 방지할 수 없다. 반드시 preventDefault를 명시적으로 호출해야 한다
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| function Form() {
function handleSubmit(e) {
e.preventDefault();
console.log('You clicked submit.');
}
return (
<form onSubmit={handleSubmit}>
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
);
}
|
캡쳐링과 버블링
- 이벤트 버블링
- 자식요소에서 발생한 이벤트가 상위의 부모요소에까지 영향을 미치는 것
- 이벤트 캡쳐링
- 버블링과는 반대로 부모요소의 이벤트가 자식요소에까지 영향을 미치는 것
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| export default function Event() {
const handleButtonClick = () => {
console.log('handleButtonClick');
};
const handleClickcaputre = () => {
console.log('handleClickcaputre');
};
const handleClickCaputre2 = () => {
console.log('handleClickCaputre2');
};
const handleClickBubble = () => {
console.log('handleClickBubble');
};
return (
<div onClickCapture={handleClickcaputre}>
<div onClickCapture={handleClickCaputre2} onClick={handleClickBubble}>
<button onClick={handleButtonClick}>Button</button>
</div>
</div>
);
}
|
제일 상위 div에서 캡쳐링 > 그 아래 div > 캡쳐링 > 버튼의 클릭이벤트 > 그 위 div의 버블링
조건부 렌더링
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| import React from 'react';
const UserGreeting = ({ name, count }) => {
return (
<h1>
{name && name + ','} Welcome {count && `Its ${count} times`}
</h1>
);
};
const GuestGreeting = () => {
return <h1>Plsease sign Up</h1>;
};
const Greeting = (props) => {
return props.isLoggedIn ? (
<UserGreeting name='jimmy' count={0} />
) : (
<GuestGreeting />
);
};
export default function Condition() {
const isLoggedIn = true;
return (
<div>
<Greeting isLoggedIn={isLoggedIn} />
</div>
);
}
|
논리연산자 && 으로 if를 인라인으로 표현하기
JavaScript에서 true && expression은 항상 expression으로 평가되고 false && expression은 항상 false로 평가됩니다
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| const UserGreeting = ({ name, count }) => {
return (
<h1>
{name && name + ','} Welcome {count && `Its ${count} times`}
</h1>
);
};
|
- name이 있을경우에 && 뒤의 name + ‘,’ 가 보인다. name이 없으면 아무것도 출력되지 않음
- falsy 표현식을 반환하면 여전히 && 뒤에 있는 표현식은 건너뛰지만 falsy 표현식이 반환된다는 것에 주의하라
- count에 0이 들어가면 내용이 안나오는게 아닌 0이 렌더링 된다

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| const UserGreeting = ({ name, count }) => {
return (
<h1>
{name && name + ','} Welcome {Boolean(count) && `Its ${count} times`}
</h1>
);
};
|
- count를 Boolean으로 감싸서 falsy를 false로 만든다 => 아무것도 출력되지 않는다
- 삼항연산자를 쓸 수도 있다
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| const UserGreeting = ({ name, count }) => {
return (
<h1>
{name && name + ','} Welcome {count ? `Its ${count} times` : null}
</h1>
);
};
|

List 와 Key
- default key => key를 안주면 react는 index를 쓴다(워닝 O)
- 고유성 => 형제 사이에서만 고유하면 된다
- key props => key는 props로 넘어가지 않음
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| const todos = [
{ id: 1, text: '아침먹기' },
{ id: 2, text: '점심먹기' },
{ id: 3, text: '저녁먹기' },
{ id: 4, text: '간식먹기' },
];
const Item = (props) => {
)
return <li>{props.text}</li>;
};
const TodoList = () =>
todos.map((todo) => <Item key={todo.id} text={todo.text} />);
export default function List() {
return (
<>
<TodoList />
</>
);
}
|



